One year prognosis of chronic complete occlusive disease after percutaneous coronary intervention
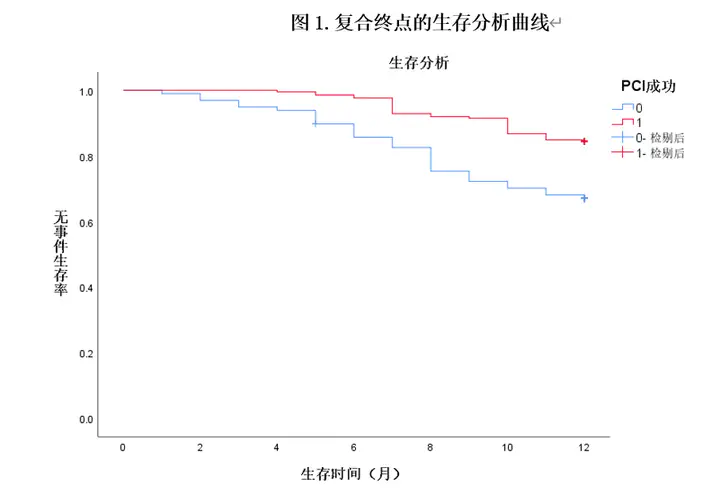 Kaplan-Meier Survival Curves for MACE Events (Red Line for Successful PCI Patients, Blue Line for PCI Failure Patients)
Kaplan-Meier Survival Curves for MACE Events (Red Line for Successful PCI Patients, Blue Line for PCI Failure Patients)Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) to open chronic total occlusive lesions (CTO) on patients’ cardiac structure and function, to assess the benefits of surgical treatment, and to provide guidance for individualizing clinical treatment plans.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 310 patients with CTO detected by coronary angiography at the Central South Hospital of Wuhan University from January 2019 to June 2021 was performed. Patients were observed by outpatient follow-up records or telephone follow-up, and the occurrence of primary and secondary endpoint events were recorded, and structural changes in the heart were understood based on cardiac ultrasound results at one year of follow-up.
Results: The 1-year follow-up study of patients in the PCI failure group showed a significantly higher rate of endpoint events than in the successful PCI group (29.59% vs. 15.57% ,p < 0.05), and the frequency of adverse cardiovascular events and the rate of revascularization were significantly higher in the PCI failure group than in the PCI The frequency of adverse cardiovascular events and re-vascularization rate were significantly higher in the failed PCI group than in the successful PCI group. In 108 of these patients, cardiac ultrasound results were reviewed, and paired analysis showed that the left atrial internal diameter and left ventricular end-diastolic internal diameter of patients in the successful PCI-opened CTO vascular offender group were significantly smaller and the left ventricular ejection fraction was significantly improved compared with that before the procedure (p values were <0.05). In-depth analysis of the effect sizes suggested that LVEF (Cohen’s d value=0.581), left atrial internal diameter (Cohen’s d value=0.854) and left ventricular end-diastolic internal diameter (Cohen’s d value=0.433) were most significantly improved in the left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF) <50% with successful PCI-opened CTO vascular offender group. Multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that successful PCI and the addition of β-blockers reduced the incidence of the primary endpoint. In contrast, SYNTAX I score >32 and preprocedural CK-MB >25 U/L were independent risk factors for the primary endpoint.
Conclusion: Opening chronic total occlusion by percutaneous coronary intervention reduces the incidence of adverse cardiovascular events and revascularization; in patients with LV ejection fraction <50%, PCI with CTO also improved LV ejection fraction, improved cardiac pump function, reduced LV internal diameter and LV end-diastolic internal diameter, and reversed ventricular remodeling.