Cohort Study:the The Relationship Between atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) and the severity of coronary artery disease (CAD)
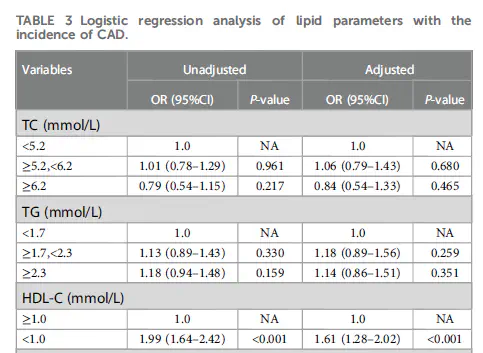 Logistic regression analysis of risk factor of SYNTAX score
Logistic regression analysis of risk factor of SYNTAX scoreIn this study, I was involved in the research design and conducted all data analysis (primarily using SPSS software)
In this project, I published an article as the co-first author
Objective: Dyslipidemia is a key risk factor for coronary artery disease (CAD). This
study aimed to investigate the correlation between the atherogenic index of
plasma (AIP) and the severity of CAD.
Methods: 2,491 patients were enrolled in this study and analyzed retrospectively,
including 665 non-CAD patients as the control group and 1,826 CAD patients.
The CAD patients were classified into three subgroups according to tertiles of
SYNTAX score (SS). Non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (Non-HDL-C) was
defined as serum total cholesterol (TC) minus serum high-density lipoprotein
cholesterol (Non-HDL-C), atherogenic index (AI) was defined as the ratio of
non-HDL-C to HDL-C; AIP was defined as the logarithm of the ratio of the
concentration of triglyceride (TG) to HDL-C; lipoprotein combine index (LCI)
was defined as the ratio of TC∗TG∗ low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL)to
HDL-C; Castelli Risk Index I (CRI I) was defined as the ratio of TC to HDL-C;
Castelli Risk Index II (CRI II) was defined as the ratio of LDL-C to HDL-C.
Results: The levels of AIP (P < 0.001), AI (P < 0.001), and LCI (P = 0.013) were higher
in the CAD group compared with the non-CAD group. The Spearman correlation
analysis showed that AIP (r = 0.075, P < 0.001), AI (r = 0.132, P < 0.001), and LCI (r =
0.072, P = 0.001) were positively correlated with SS. The multivariate logistic
regression model showed CRI I (OR: 1.11, 95% CI: 1.03–1.19, P = 0.005), CRI II
(OR: 1.26, 95% CI: 1.15–1.39, P < 0.001), AI (OR: 1.28, 95% CI: 1.17–1.40, P <
0.001), AIP (OR: 2.06, 95% CI: 1.38–3.07, P < 0.001), and LCI (OR: 1.01, 95% CI:
1.01–1.02, P < 0.001) were independent predictors of severity of CAD After
adjusting various confounders.
Conclusion: CRI I, CRI II, AIP, AI, and LCI were independent predictors of the severity
of CAD, which could be used as a biomarker for the evaluation of the severity of CAD.